Given the Following Information, What Is the Ratio of Liabilities to Stockholders Equity?
Financial Statement Analysis
Fiscal Statement Analysis
Financial statement analysis reviews financial information found on fiscal statements to make informed decisions almost the business. The income statement, statement of retained earnings, residual sheet, and statement of cash flows, among other financial information, tin be analyzed. The information obtained from this analysis can do good decision-making for internal and external stakeholders and can requite a visitor valuable data on overall performance and specific areas for comeback. The analysis tin help them with budgeting, deciding where to cut costs, how to increase revenues, and time to come capital investments opportunities.
When because the outcomes from analysis, it is important for a company to understand that data produced needs to be compared to others within industry and shut competitors. The visitor should likewise consider their by experience and how it corresponds to current and futurity functioning expectations. 3 common analysis tools are used for controlling; horizontal analysis, vertical assay, and financial ratios.
For our give-and-take of financial statement analysis, nosotros will employ Banyan Appurtenances. Banyan Appurtenances is a merchandising company that sells a variety of products. (Figure) shows the comparative income statements and balance sheets for the past two years.
Comparative Income Statements and Residual Sheets.
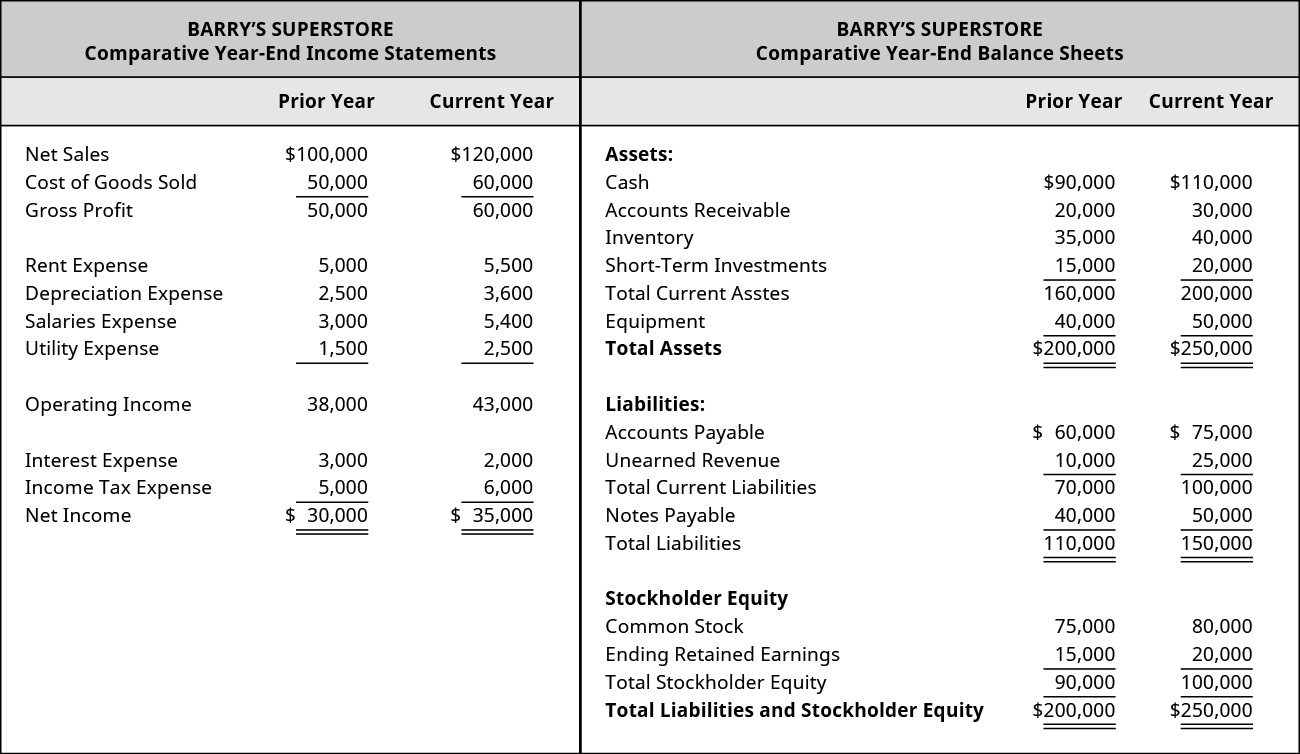
Keep in mind that the comparative income statements and residue sheets for Banyan Goods are simplified for our calculations and practise not fully represent all the accounts a company could maintain. Allow's begin our analysis discussion by looking at horizontal assay.
Horizontal Analysis
Horizontal analysis (besides known as trend assay) looks at trends over fourth dimension on various fiscal statement line items. A visitor volition look at one menses (usually a year) and compare it to some other period. For example, a company may compare sales from their electric current year to sales from the prior yr. The trending of items on these financial statements can requite a company valuable information on overall performance and specific areas for improvement. It is well-nigh valuable to do horizontal analysis for information over multiple periods to see how change is occurring for each line item. If multiple periods are not used, it tin be hard to identify a trend. The year beingness used for comparison purposes is called the base of operations year (usually the prior period). The yr of comparison for horizontal analysis is analyzed for dollar and percentage changes against the base twelvemonth.
The dollar change is found past taking the dollar amount in the base year and subtracting that from the year of analysis.

Using Banyan Goods equally our case, if Banyan wanted to compare cyberspace sales in the current twelvemonth (year of assay) of ?120,000 to the prior year (base twelvemonth) of ?100,000, the dollar change would exist equally follows:
\(\text{Dollar modify}=?120,000–?1000,000=?20,000\)
The percentage alter is institute by taking the dollar alter, dividing by the base of operations year corporeality, and so multiplying by 100.

Let's compute the percentage change for Banyan Goods' cyberspace sales.
\(\text{Percent modify}=\left(\frac{?20,000}{?100,000}\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}×\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}100=20%\)
This means Banyan Appurtenances saw an increase of ?xx,000 in net sales in the current year equally compared to the prior year, which was a twenty% increase. The same dollar change and percentage modify calculations would be used for the income statement line items as well as the balance sheet line items. (Figure) shows the complete horizontal analysis of the income statement and balance sheet for Banyan Goods.
Income Statements and Horizontal Assay.
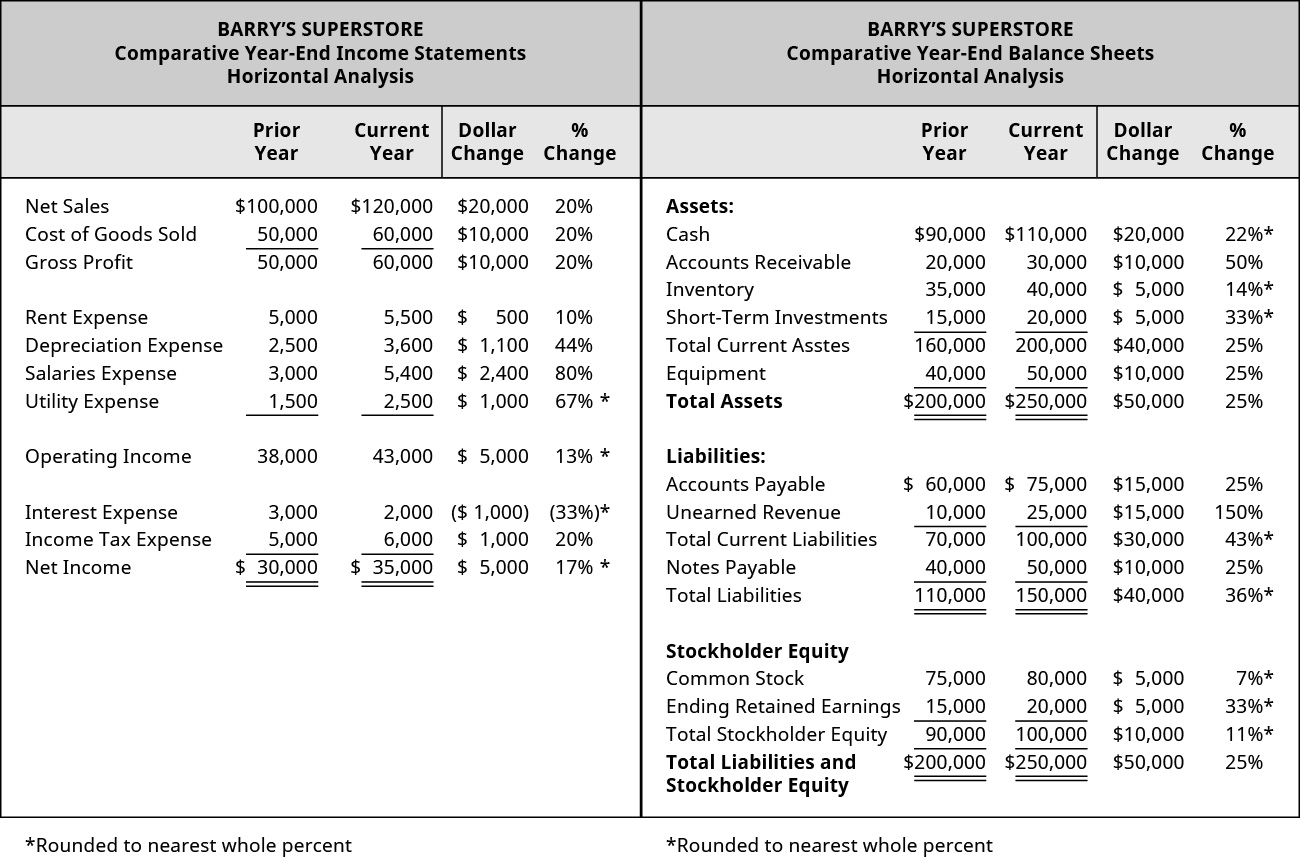
Depending on their expectations, Banyan Goods could make decisions to alter operations to produce expected outcomes. For example, Banyan saw a fifty% accounts receivable increment from the prior yr to the current year. If they were only expecting a 20% increment, they may need to explore this line item farther to decide what caused this difference and how to correct information technology going forrard. It could mayhap exist that they are extending credit more than readily than predictable or not collecting equally apace on outstanding accounts receivable. The visitor will need to further examine this difference earlier deciding on a course of activity. Some other method of analysis Banyan might consider before making a decision is vertical assay.
Vertical Analysis
Vertical analysis shows a comparison of a line item inside a statement to another line item inside that same statement. For example, a company may compare cash to total assets in the current twelvemonth. This allows a visitor to see what percentage of cash (the comparison line particular) makes up full assets (the other line item) during the period. This is different from horizontal analysis, which compares beyond years. Vertical analysis compares line items within a argument in the current twelvemonth. This can help a business to know how much of one particular is contributing to overall operations. For example, a visitor may want to know how much inventory contributes to full assets. They can and then employ this information to brand business decisions such every bit preparing the budget, cutting costs, increasing revenues, or upper-case letter investments.
The company will need to determine which line particular they are comparing all items to inside that statement and and then calculate the pct makeup. These percentages are considered common-size because they make businesses within industry comparable by taking out fluctuations for size. It is typical for an income statement to use net sales (or sales) as the comparison line detail. This means net sales will exist fix at 100% and all other line items inside the income statement will represent a percentage of net sales.
On the balance sheet, a company will typically look at two areas: (ane) full assets, and (ii) total liabilities and stockholders' equity. Total assets will exist set at 100% and all assets will represent a pct of total avails. Total liabilities and stockholders' equity will also exist set at 100% and all line items inside liabilities and disinterestedness volition be represented as a percentage of full liabilities and stockholders' equity. The line detail set at 100% is considered the base amount and the comparison line particular is considered the comparison amount. The formula to determine the mutual-size percentage is:
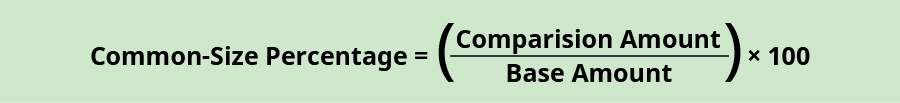
For case, if Banyan Goods set total assets equally the base corporeality and wanted to meet what percentage of total assets were made upwards of cash in the current year, the following calculation would occur.
\(\text{Mutual-size per centum}=\left(\frac{?110,000}{?250,000}\right)\phantom{\dominion{0.2em}{0ex}}×\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}100=44%\)
Cash in the current twelvemonth is ?110,000 and total assets equal ?250,000, giving a common-size per centum of 44%. If the company had an expected greenbacks balance of twoscore% of total avails, they would be exceeding expectations. This may not be plenty of a difference to make a modify, but if they notice this deviates from industry standards, they may need to make adjustments, such equally reducing the corporeality of cash on hand to reinvest in the business. (Effigy) shows the common-size calculations on the comparative income statements and comparative balance sheets for Banyan Goods.
Income Statements and Vertical Analysis.
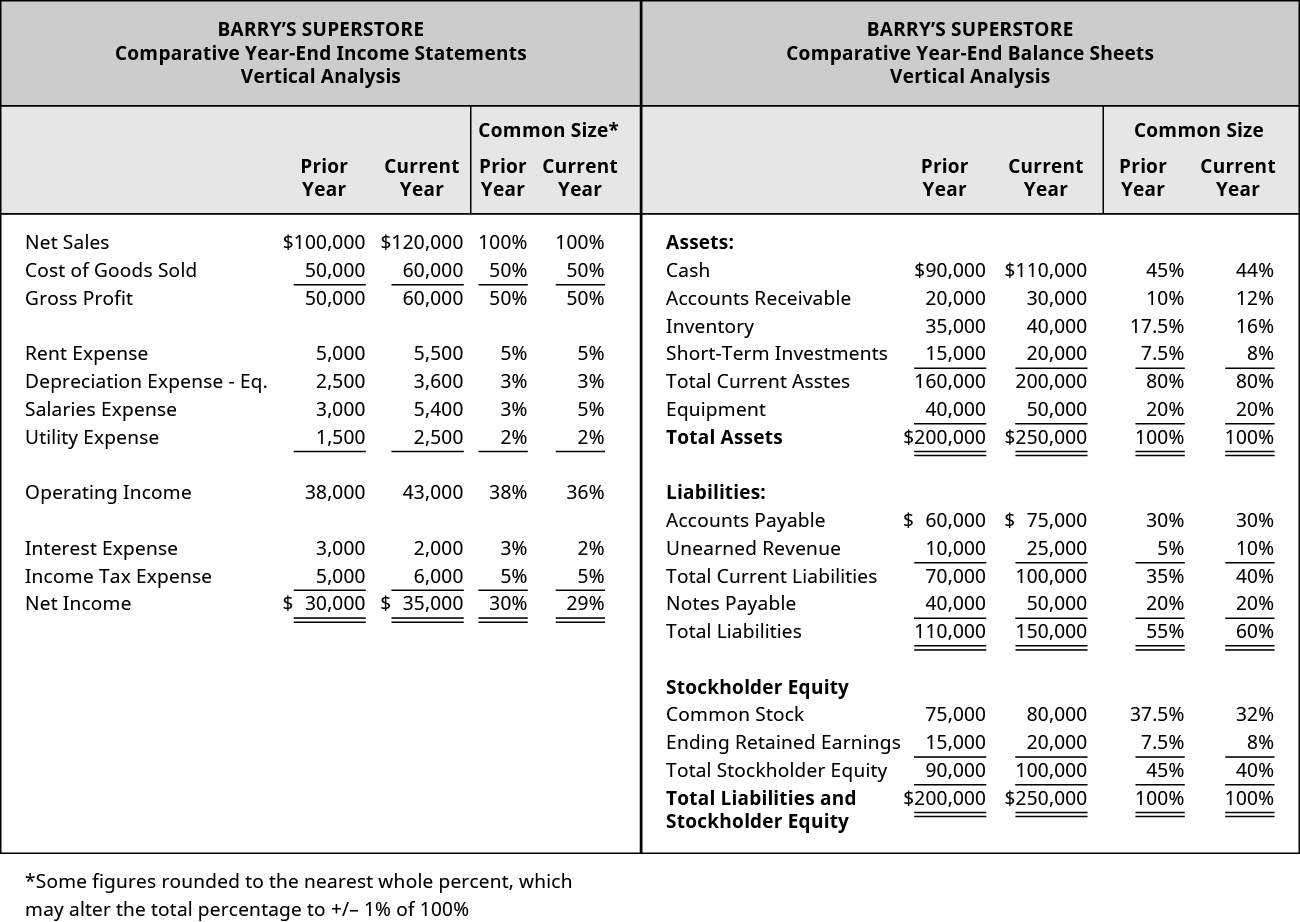
Fifty-fifty though vertical analysis is a statement comparison within the same year, Banyan can utilise information from the prior year'due south vertical analysis to make sure the business organisation is operating as expected. For example, unearned revenues increased from the prior year to the current year and made up a larger portion of full liabilities and stockholders' equity. This could be due to many factors, and Banyan Goods will need to examine this further to see why this alter has occurred. Allow'due south plough to financial statement analysis using financial ratios.
Overview of Financial Ratios
Financial ratios help both internal and external users of data make informed decisions about a company. A stakeholder could exist looking to invest, become a supplier, make a loan, or alter internal operations, among other things, based in part on the outcomes of ratio assay. The information resulting from ratio analysis can be used to examine trends in operation, found benchmarks for success, set upkeep expectations, and compare industry competitors. There are four main categories of ratios: liquidity, solvency, efficiency, and profitability. Notation that while in that location are more ideal outcomes for some ratios, the industry in which the business operates can modify the influence each of these outcomes has over stakeholder decisions. (You will learn more about ratios, industry standards, and ratio estimation in advanced bookkeeping courses.)
Liquidity Ratios
Liquidity ratios prove the ability of the company to pay short-term obligations if they came due immediately with assets that tin can be quickly converted to cash. This is washed by comparing electric current assets to current liabilities. Lenders, for example, may consider the outcomes of liquidity ratios when deciding whether to extend a loan to a company. A company would like to exist liquid enough to manage whatsoever currently due obligations but non also liquid where they may not be effectively investing in growth opportunities. 3 mutual liquidity measurements are working capital, current ratio, and quick ratio.
Working Capital
Working capital measures the financial health of an organisation in the curt-term by finding the difference between electric current assets and current liabilities. A company will demand plenty electric current assets to cover current liabilities; otherwise, they may not be able to proceed operations in the future. Before a lender extends credit, they will review the working uppercase of the company to run across if the company can meet their obligations. A larger difference signals that a company can cover their short-term debts and a lender may be more willing to extend the loan. On the other hand, too large of a difference may signal that the company may non be correctly using their assets to grow the business organization. The formula for working capital is:

Using Banyan Goods, working capital is computed as follows for the current twelvemonth:
\(\text{Working majuscule}=?200,000–?100,000=?100,000\)
In this case, current avails were ?200,000, and current liabilities were ?100,000. Current assets were far greater than current liabilities for Banyan Goods and they would easily exist able to cover curt-term debt.
The dollar value of the difference for working capital is limited given visitor size and scope. Information technology is most useful to convert this information to a ratio to determine the company's electric current financial health. This ratio is the current ratio.
Electric current Ratio
Working capital expressed equally a ratio is the current ratio. The current ratio considers the amount of current assets available to cover current liabilities. The higher the electric current ratio, the more likely the visitor can cover its brusque-term debt. The formula for current ratio is:
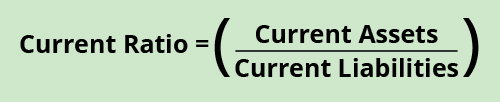
The current ratio in the current year for Banyan Goods is:
\(\text{Current ratio}=\left(\frac{?200,000}{?100,000}\correct)=\text{ii or 2:ane}\)
A ii:ane ratio ways the company has twice equally many current assets every bit electric current liabilities; typically, this would be enough to cover obligations. This may be an acceptable ratio for Banyan Goods, merely if it is besides high, they may want to consider using those assets in a different way to abound the company.
Quick Ratio
The quick ratio, likewise known as the acid-test ratio, is similar to the current ratio except electric current assets are more narrowly defined equally the near liquid assets, which exclude inventory and prepaid expenses. The conversion of inventory and prepaid expenses to cash can sometimes take more time than the liquidation of other current avails. A visitor will want to know what they accept on hand and can utilise apace if an immediate obligation is due. The formula for the quick ratio is:

The quick ratio for Banyan Goods in the electric current year is:
\(\text{Quick ratio}=\left(\frac{?110,000+?20,000+?thirty,000}{?100,000}\correct)=\text{1.6 or one.6:1}\)
A 1.vi:ane ratio means the company has enough quick assets to cover electric current liabilities.
Some other category of financial measurement uses solvency ratios.
Solvency Ratios
Solvency implies that a company can meet its long-term obligations and volition likely stay in business in the future. To stay in business the company must generate more revenue than debt in the long-term. Meeting long-term obligations includes the ability to pay whatsoever interest incurred on long-term debt. Ii primary solvency ratios are the debt-to-disinterestedness ratio and the times interest earned ratio.
Debt to Disinterestedness Ratio
The debt-to-equity ratio shows the relationship betwixt debt and disinterestedness every bit it relates to business financing. A company tin can accept out loans, event stock, and retain earnings to exist used in future periods to go along operations running. Information technology is less risky and less costly to utilise equity sources for financing every bit compared to debt resource. This is mainly due to interest expense repayment that a loan carries as opposed to disinterestedness, which does not have this requirement. Therefore, a company wants to know how much debt and equity contribute to its financing. Ideally, a company would adopt more equity than debt financing. The formula for the debt to equity ratio is:
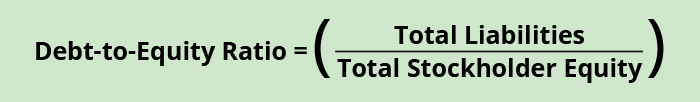
The information needed to compute the debt-to-equity ratio for Banyan Goods in the electric current year tin be found on the balance canvass.
\(\text{Debt-to-disinterestedness ratio}=\left(\frac{?150,000}{?100,000}\right)=\text{1.5 or 1.5:1}\)
This means that for every ?1 of equity contributed toward financing, ?1.fifty is contributed from lenders. This would be a business concern for Banyan Appurtenances. This could exist a red flag for potential investors that the company could exist trending toward insolvency. Banyan Appurtenances might want to go the ratio below 1:i to ameliorate their long-term business viability.
Times Interest Earned Ratio
Time interest earned measures the company'southward ability to pay interest expense on long-term debt incurred. This ability to pay is determined by the available earnings before involvement and taxes (EBIT) are deducted. These earnings are considered the operating income. Lenders will pay attention to this ratio before extending credit. The more times over a company can cover interest, the more likely a lender will extend long-term credit. The formula for times interest earned is:

The information needed to compute times interest earned for Banyan Appurtenances in the current yr can be found on the income statement.
\(\text{Times interest earned}=\left(\frac{?43,000}{?2,000}\right)=21.v\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{times}\)
The ?43,000 is the operating income, representing earnings earlier involvement and taxes. The 21.v times outcome suggests that Banyan Goods tin can easily repay interest on an outstanding loan and creditors would take piddling chance that Banyan Appurtenances would be unable to pay.
Another category of fiscal measurement uses efficiency ratios.
Efficiency Ratios
Efficiency shows how well a company uses and manages their assets. Areas of importance with efficiency are management of sales, accounts receivable, and inventory. A company that is efficient typically will exist able to generate revenues quickly using the assets information technology acquires. Let'southward examine four efficiency ratios: accounts receivable turnover, total nugget turnover, inventory turnover, and days' sales in inventory.
Accounts Receivable Turnover
Accounts receivable turnover measures how many times in a catamenia (usually a year) a company will collect cash from accounts receivable. A college number of times could mean cash is collected more apace and that credit customers are of high quality. A higher number is normally preferable because the cash collected can be reinvested in the business at a quicker charge per unit. A lower number of times could mean cash is collected slowly on these accounts and customers may non be properly qualified to take the debt. The formula for accounts receivable turnover is:

Many companies practise non split credit and greenbacks sales, in which example net sales would be used to compute accounts receivable turnover. Average accounts receivable is plant by dividing the sum of outset and catastrophe accounts receivable balances institute on the balance sail. The outset accounts receivable balance in the electric current yr is taken from the catastrophe accounts receivable residuum in the prior twelvemonth.
When computing the accounts receivable turnover for Banyan Goods, allow's assume internet credit sales make up ?100,000 of the ?120,000 of the internet sales found on the income statement in the electric current year.
\(\begin{array}{ccc}\hfill \text{Average accounts receivable}& =\hfill & \frac{?20,000+?thirty,000}{two}=?25,000\hfill \\ \hfill \text{Accounts receivable turnover}& =\hfill & \frac{?100,000}{?25,000}=\text{4 times}\hfill \end{array}\)
An accounts receivable turnover of four times per year may be low for Banyan Goods. Given this event, they may want to consider stricter credit lending practices to make sure credit customers are of a college quality. They may too need to exist more ambitious with collecting any outstanding accounts.
Total Asset Turnover
Total asset turnover measures the ability of a company to apply their avails to generate revenues. A company would like to use equally few avails as possible to generate the most net sales. Therefore, a higher full nugget turnover means the company is using their assets very efficiently to produce net sales. The formula for total nugget turnover is:
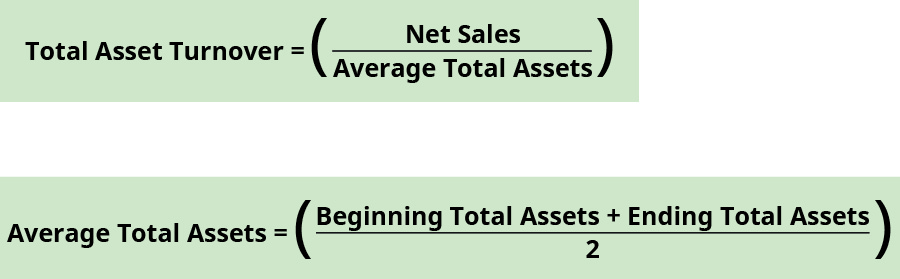
Average full avails are constitute past dividing the sum of beginning and ending full assets balances found on the balance sheet. The beginning full assets residuum in the current yr is taken from the catastrophe total assets balance in the prior twelvemonth.
Banyan Goods' full asset turnover is:
\(\begin{array}{ccc}\hfill \text{Average total assets}& =\hfill & \frac{?200,000+?250,000}{2}=?225,000\hfill \\ \hfill \text{Full assets turnover}& =\hfill & \frac{?120,000}{?225,000}=0.53\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{times (rounded)}\hfill \end{array}\)
The effect of 0.53 means that for every ?one of avails, ?0.53 of net sales are generated. Over time, Banyan Goods would similar to see this turnover ratio increase.
Inventory Turnover
Inventory turnover measures how many times during the twelvemonth a company has sold and replaced inventory. This tin can tell a company how well inventory is managed. A higher ratio is preferable; however, an extremely high turnover may mean that the company does not have enough inventory available to meet need. A low turnover may hateful the visitor has too much supply of inventory on mitt. The formula for inventory turnover is:
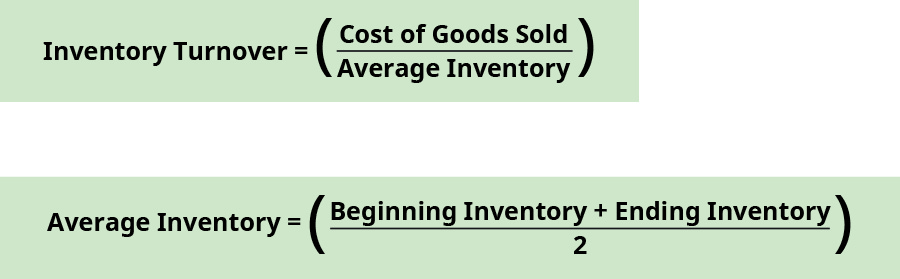
Cost of appurtenances sold for the electric current year is found on the income argument. Average inventory is found past dividing the sum of showtime and ending inventory balances found on the balance sheet. The beginning inventory balance in the current year is taken from the ending inventory residuum in the prior year.
Banyan Goods' inventory turnover is:
\(\begin{array}{ccc}\hfill \text{Average inventory}& =\hfill & \frac{?35,000+?40,000}{2}=?37,500\hfill \\ \hfill \text{Inventory turnover}& =\hfill & \frac{?60,000}{?37,500}=ane.half-dozen\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{times}\hfill \terminate{array}\)
1.6 times is a very low turnover rate for Banyan Goods. This may hateful the company is maintaining also loftier an inventory supply to meet a low demand from customers. They may want to decrease their on-manus inventory to gratis upwardly more liquid assets to apply in other ways.
Days' Sales in Inventory
Days' sales in inventory expresses the number of days it takes a company to turn inventory into sales. This assumes that no new purchase of inventory occurred within that time period. The fewer the number of days, the more quickly the company can sell its inventory. The higher the number of days, the longer information technology takes to sell its inventory. The formula for days' sales in inventory is:
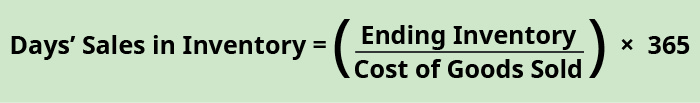
Banyan Appurtenances' days' sales in inventory is:
\(\text{Days' sales in inventory}=\left(\frac{?40,000}{?lx,000}\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}×\phantom{\dominion{0.2em}{0ex}}365=243\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{days (rounded)}\)
243 days is a long fourth dimension to sell inventory. While industry dictates what is an acceptable number of days to sell inventory, 243 days is unsustainable long-term. Banyan Goods volition need to ameliorate manage their inventory and sales strategies to move inventory more than quickly.
The final category of financial measurement examines profitability ratios.
Profitability Ratios
Profitability considers how well a company produces returns given their operational performance. The visitor needs to leverage its operations to increase profit. To help with profit goal attainment, company revenues need to outweigh expenses. Let's consider three profitability measurements and ratios: profit margin, return on total avails, and render on disinterestedness.
Profit Margin
Turn a profit margin represents how much of sales revenue has translated into income. This ratio shows how much of each ?ane of sales is returned as profit. The larger the ratio effigy (the closer it gets to 1), the more of each sales dollar is returned as turn a profit. The portion of the sales dollar not returned equally turn a profit goes toward expenses. The formula for profit margin is:
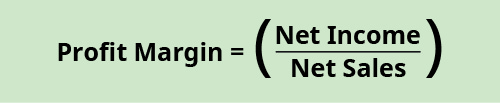
For Banyan Appurtenances, the profit margin in the current twelvemonth is:
\(\text{Profit margin}=\left(\frac{?35,000}{?120,000}\right)=0.29\phantom{\dominion{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{(rounded)}\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{or}\phantom{\dominion{0.2em}{0ex}}29%\)
This means that for every dollar of sales, ?0.29 returns as profit. If Banyan Goods thinks this is besides low, the company would try and find ways to reduce expenses and increment sales.
Return on Total Assets
The render on total assets measures the company's power to use its assets successfully to generate a turn a profit. The higher the return (ratio outcome), the more turn a profit is created from nugget utilise. Average full assets are found past dividing the sum of beginning and catastrophe total assets balances plant on the residuum sheet. The beginning total assets balance in the current year is taken from the ending total assets balance in the prior twelvemonth. The formula for render on total assets is:
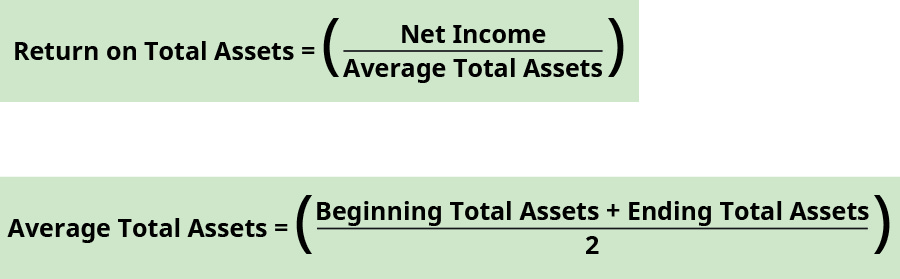
For Banyan Goods, the render on total assets for the current year is:
\(\begin{array}{ccc}\hfill \text{Average total assets}& =\hfill & \frac{?200,000+?250,000}{2}=?225,000\hfill \\ \hfill \text{Return on total assets}& =\hfill & \frac{?35,000}{?225,000}=0.sixteen\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{(rounded) or 16%}\hfill \cease{array}\)
The higher the effigy, the better the company is using its assets to create a profit. Manufacture standards tin can dictate what is an adequate return.
Return on Equity
Return on equity measures the company's ability to use its invested capital to generate income. The invested upper-case letter comes from stockholders investments in the visitor's stock and its retained earnings and is leveraged to create profit. The higher the render, the better the company is doing at using its investments to yield a turn a profit. The formula for return on equity is:
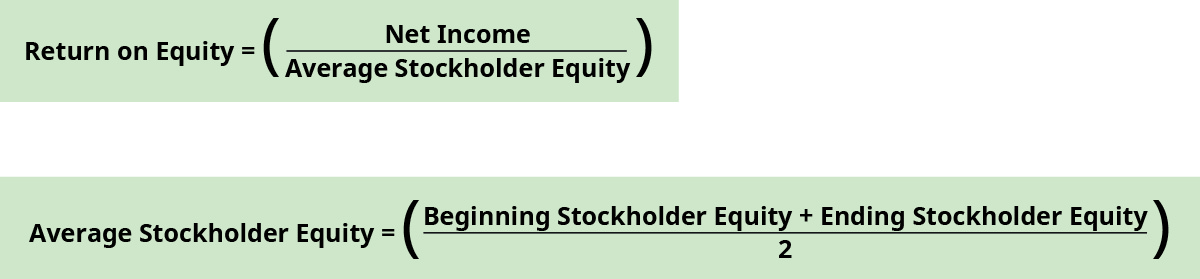
Average stockholders' equity is found by dividing the sum of beginning and catastrophe stockholders' equity balances plant on the balance canvass. The offset stockholders' equity balance in the current year is taken from the ending stockholders' equity balance in the prior year. Continue in mind that the internet income is calculated after preferred dividends have been paid.
For Banyan Goods, nosotros will apply the internet income effigy and assume no preferred dividends have been paid. The return on equity for the current year is:
\(\begin{array}{ccc}\hfill \text{Average stockholder equity}& =\hfill & \frac{?90,000+?100,000}{2}=?95,000\hfill \\ \hfill \text{Render on equity}& =\hfill & \frac{?35,000}{?95,000}=0.37\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{(rounded) or 37%}\hfill \end{array}\)
The higher the effigy, the meliorate the company is using its investments to create a turn a profit. Industry standards can dictate what is an acceptable return.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Financial Statement Analysis
At that place are several advantages and disadvantages to fiscal statement analysis. Financial statement analysis can bear witness trends over time, which can be helpful in making time to come business decisions. Converting information to percentages or ratios eliminates some of the disparity betwixt competitor sizes and operating abilities, making it easier for stakeholders to make informed decisions. It can assist with agreement the makeup of current operations within the business, and which shifts need to occur internally to increment productivity.
A stakeholder needs to proceed in mind that past performance does non always dictate hereafter operation. Attention must be given to possible economic influences that could skew the numbers beingness analyzed, such as inflation or a recession. Additionally, the mode a company reports data within accounts may change over time. For instance, where and when certain transactions are recorded may shift, which may not be readily evident in the financial statements.
A visitor that wants to budget properly, command costs, increase revenues, and make long-term expenditure decisions may want to use fiscal argument assay to guide future operations. As long as the visitor understands the limitations of the information provided, fiscal statement analysis is a skillful tool to predict growth and company financial forcefulness.
Source: https://opentextbc.ca/principlesofaccountingv1openstax/back-matter/financial-statement-analysis/
0 Response to "Given the Following Information, What Is the Ratio of Liabilities to Stockholders Equity?"
Post a Comment